Set Up Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager Cloud Management Gateway (MECM-CMG) in 5 Steps
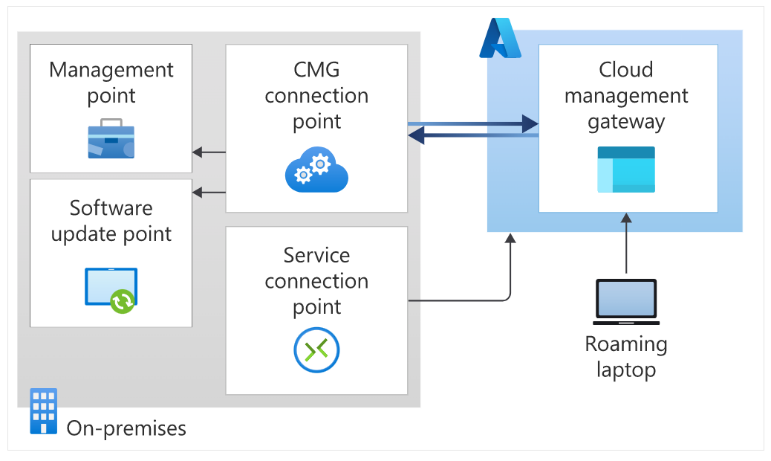
The Cloud Management Gateway (CMG) is designed to support devices that are Configuration Manager clients and not connected or reachable within corporate networks. In addition to providing management capabilities, updates, servicing, and task sequences, the CMG can seamlessly connect to Azure cloud resources over the internet without the use of VPNs (virtual private networks).
This allows users to manage clients that roam on the internet or are in branch offices across the WAN, without exposing your on-premises infrastructure to the internet.
While this blog is not intended to be an exhaustive ‘how to article,’ we hope to clarify the setup for the design decision process so users can get up and running quickly and start testing the available options in a single instance lab configuration.
Recommended Configurations
Before you begin, we recommend that you make the following configurations:
- Enable AD-Connect hybrid devices if you have not already done so
- This is the only CMG authentication option that enables user targeting when configuring hybrid managed devices
- This process automatically adds the targeted devices to Azure AD as Hybrid Azure Active Directory Domain Joined (HAADJ) when configured by GPO or Client policy
- This filtering should specify or exclude specific OUs (Organizational Units) at first, so the entire domain worth of devices (and servers) is not imported, as is recommended in most Hybrid enablement cases
- Filter the devices allowed to manually join Azure AD to limit rogue and unintended devices from enrolling
- Use Enhanced Http (which is required by current releases of Configuration Manager 2013 and greater) to use a primary site without converting it to https PKI (Public Key Infrastructure)
- Define the boundaries and boundary groups for the VPN and test clients using standard practices
- Assign the Distribution point and Distribution point group to use Microsoft cloud resources where possible
5 Steps to Configuring the Cloud Management Gateway
- Certificate Creation
There are 2 certificates required, one for the server connection to Azure and the other for the client. This can be completed on an internal PKI, or you can use a more public facing root cert provider. The requirement to extend a Configuration Manager Resource to Azure AD is dependent on the root certificate(s).
- Create the cloud certificate(s)
- Request the certificate on the Configuration Manager Server
-There is a service name required when requesting the certificate from the CA (Certificate Authorities)
-The naming convention would need a unique service name added as the Common Name
(CN) properties during creation (at the time of the Certificate request):
<service name>.<AZURE region>.cloudapp.azure.com
-This will be auto populated later in the setup CMG Wizard when the certificate is imported
- Export the certificate locally for the CMG Setup
- Configure the client certificate
- Azure Application Setup
Note: You will need an Azure subscription owner role to set this up.
In the Azure Services mode, you can pre-create the AD application using default options and a unique hostname.

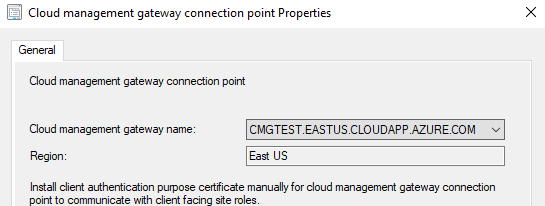
- Cloud Management Gateway Setup
Configure the CMG in console:
- Import previously created Root certificate
- Select VM (Virtual Machine) Scale Set sizing and capacity
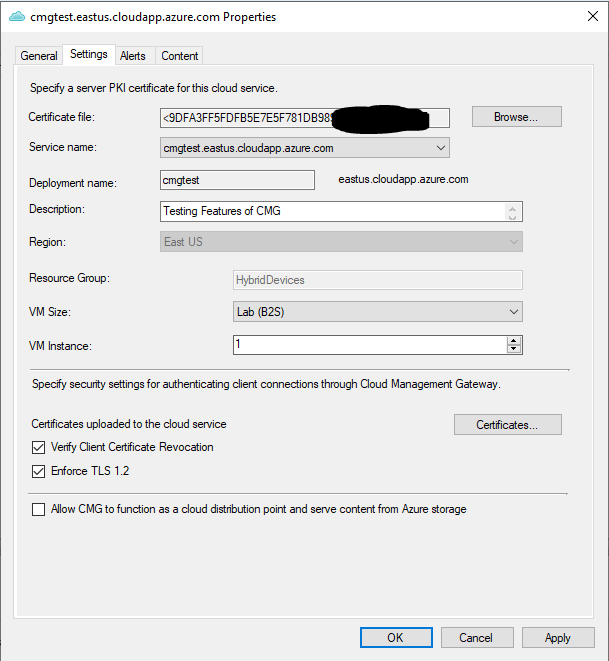
Note: The options to select a VM and instances needed can be resized later. If you are only testing, the lab option provided would be suitable.
- Add the Configuration Manager Role
This configuration is adding the Cloud Management Gateway Role to the site server. It will auto-populate a detected instance of the Azure Application.
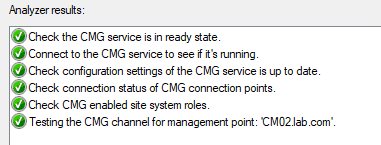
Once you are setup, you can check the service health to ensure that you are properly configured (up until this point) by right-clicking on the new service created.
- Client Configuration
The client will get the latest information for the CMG URL when the management point info updates on the client side and the root certificate is auto enrolled on the workstation during the next log on or reboot cycle.
Note: Reboot the test system when connected on-prem or through VPN (virtual private network) to expedite a full policy update.
Next Steps: Client Deployment
In this scenario, we took steps to complete AD-Connect Hybrid device enrollment and the client that was pre-existing was not modified. The client can be installed as usual to support the new configurations.
Once CMG is deployed and configured, clients can seamlessly access on-premises site roles whether they’re on the intranet or internet.
To learn more about MECM-CMG, check out our recent blog:
Microsoft’s Cloud Management Gateway (CMG): 8 of Our Most Frequently Asked Questions
Contact an Arraya expert today to get started or should you have any questions.
Visit https://www.arrayasolutions.com//contact-us/ to connect with our team now.
Comment on this and all of our posts on: LinkedIn, Twitter and Facebook.
Follow us to stay up to date on our industry insights and unique IT learning opportunities.
